OUTLINE
- What is blockchain?
- How does it work?
- Why you should know about blockchain?
- What Blockchain Technology Is Used For?
- How can it be used in the wider enterprise?
- The most prominent advantages/value of Blockchain.
- The future of Blockchain.
What is Blockchain?
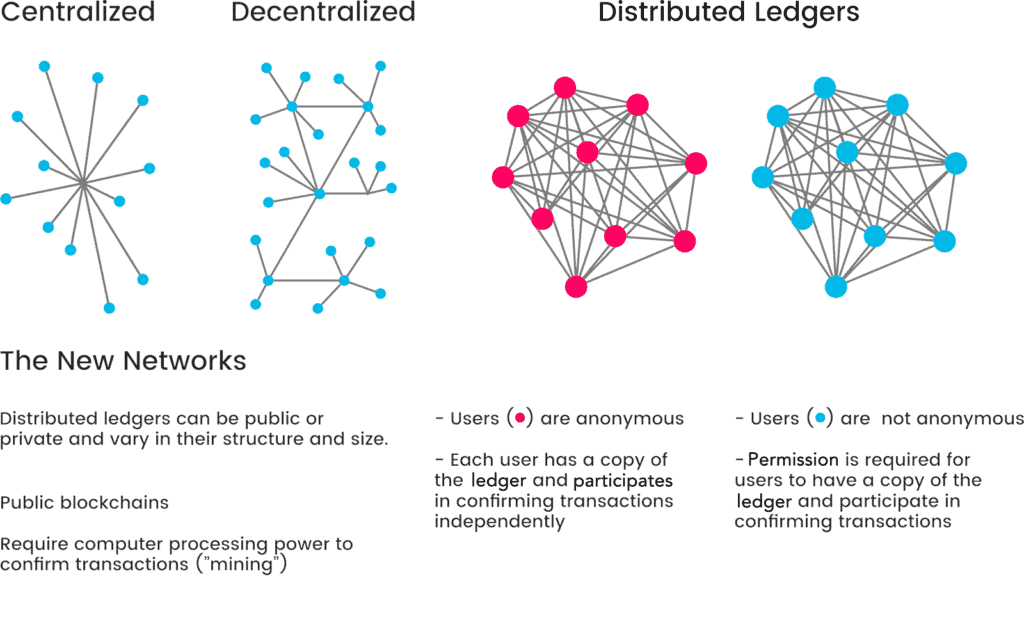
Blockchain technology operates as a common, cryptographically verified ledger, distributed across a broad decentralized network of computers (or nodes), largely known for its use in recording value transactions and exchanges.
Each ledger entry is considered a “block” in the broader “chain,” and each block is cryptographically validated by a consensus-based algorithm which is computed across the node network.
Each block is not added to the chain until a mathematical consensus is achieved – this is the distributed function that effectively replaces a centralized “clearing house”.
The chief advantage that a distributed, decentralized ledger offers over, say, a ledger hosted by a central server, is that it is not controlled by a single entity, and therefore is theoretically immutable and tamper-proof.
This aspect of blockchain lends itself to a wide variety of use cases in which “trust” is paramount. Cryptocurrency is just one obvious use case, given the value of a currency is driven by trust.
Blockchain is also particularly well suited for “attestation”, i.e. saying “This is you, and everything associated with you is attached to this chain” and it uses cryptography instead of a central “clearing house” to certify that a piece of information on the chain is true and the blockchain itself, once the initial attestation is done, is inherently trustworthy without the need to know, verify or expose anything about you beyond the requested data.
In the context of data privacy, for instance, I can give my birthday to you and only you without exposing my whole driver’s license to you and without exposing my birthday to anyone OTHER than you (FYI – handing your Driver’s License to someone to validate your birthday actually exposes a TON of information about you for no good reason).
A “block” works like this BLOCK – Data(hello world) – Previous hash – Hash(this is like a fingerprint)
Every member of a blockchain database has a copy of the full chain and receives each new block one by one. Unlike a centralized database that could be altered from one primary location, any tampering with a blockchain would notify every member of the database that something has been altered.
While technically a Blockchain implementation can exist without the need for a cryptocurrency (Bitcoin) in a private environment, they generally become the requirement in a public Blockchain due to the fact that they are used as rewards for miners to uphold the decentralized database.
How does Blockchain work?
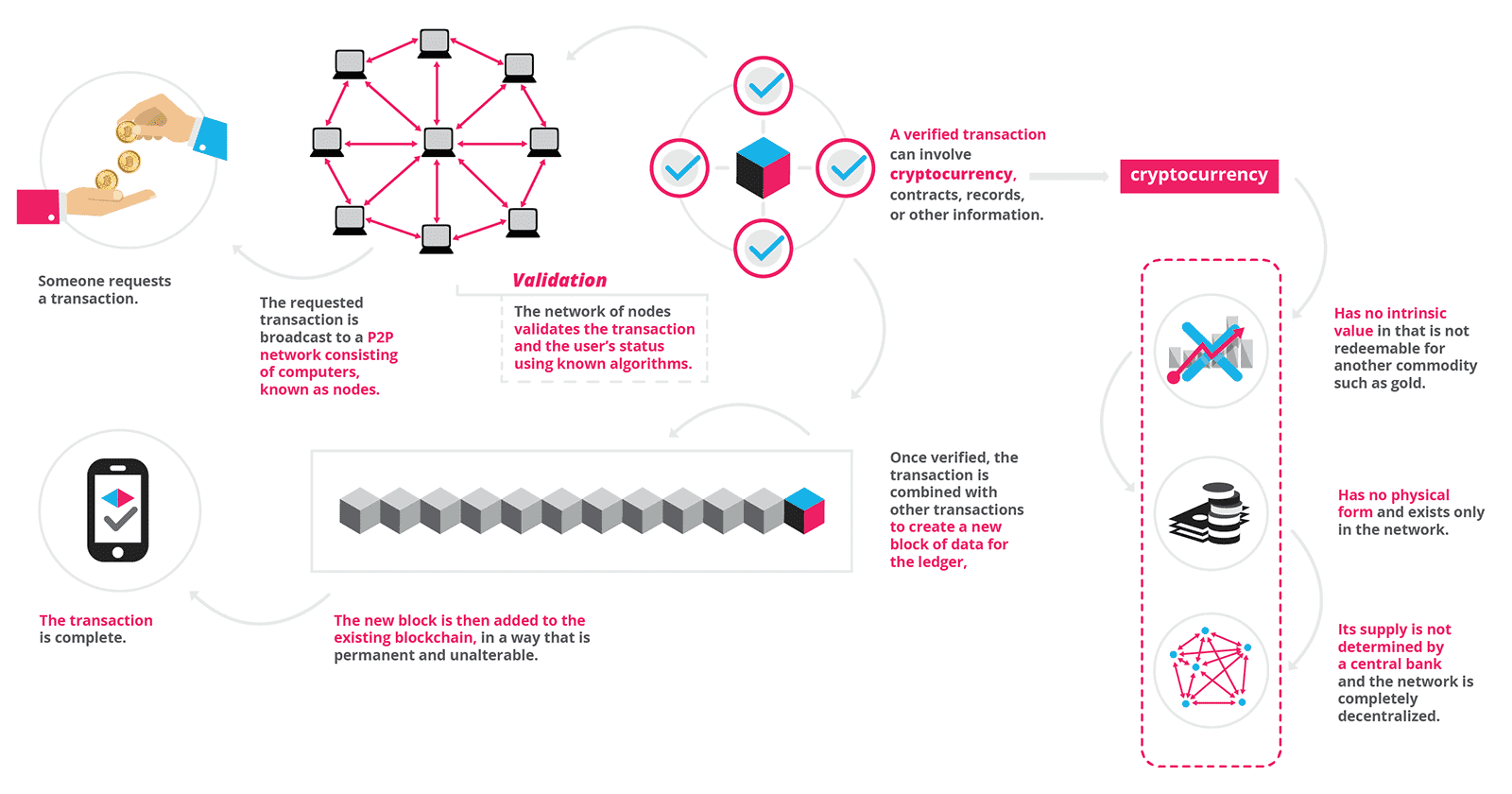
The blockchain is an interconnection of different nodes. All data in a Blockchain is represented as blocks. Each separate transaction means that a new block is created in a Blockchain.
A Blockchain records data linearly which means that every new block contains information from all previous blocks in addition to the new data that is being added.
A block stores multiple of transactions, each block is made up of a ledger of information which could be a date and time, and encrypts information with the help of complex algorithms.
When a party submits a change to an existing transaction or new transaction on the ledger, it must be approved and validated by another party before the transaction can be officially added to the blockchain network.
This means every participant of the network has a copy of the blockchain. Therefore, if an attacker modifies the blockchain on one of the computers in the network, they are modifying only one single copy of the blockchain.
The network will see this, compare it with the prevailing majority of versions of the blockchain in the network, and quickly override it.
An attacker can only hack into a blockchain when it takes control of 50-55% of the network.
Blockchain transactions are completed through what is known as “smart contracts”—i.e. automated contracts that transfer funds in cryptocurrency once certain conditions are met.
So, every time a change occurs on the blockchain, say I send you some cryptocurrency (perhaps a KeyoCoin token to reward you for staying at my hotel), a new line is written into that database, confirming that I have ceded possession of one KeyoCoin, and you now own it.
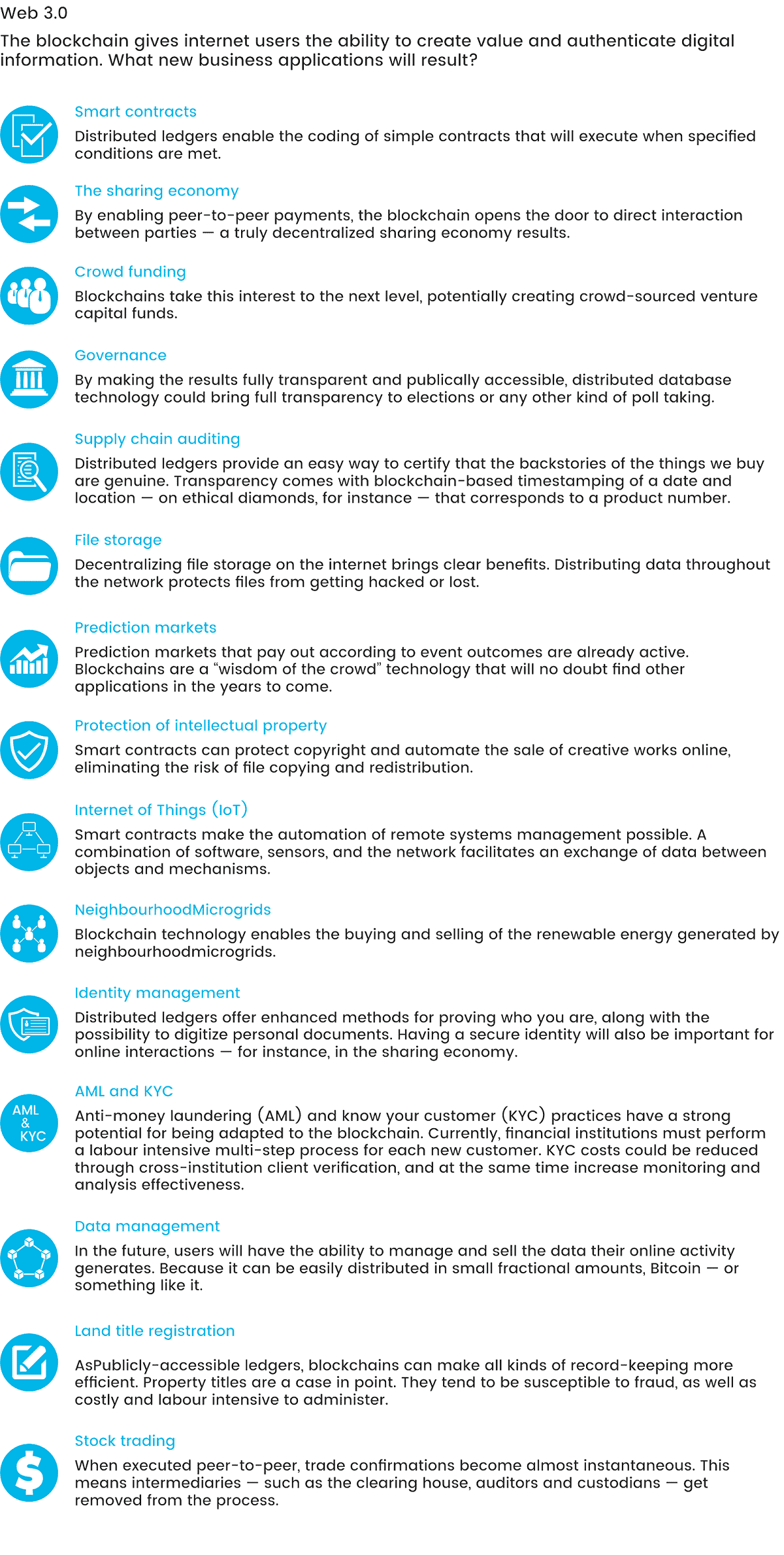
Blockchain Technology can be applied in the following ways:
To manage customer identity and data privately and securely.
To store important financial records in a decentralized (and encrypted) network.
To reduce human error and make processes (such as dispute resolutions) much more efficient.
This is an infographic view of how blockchain works
You may also be interested in Best Crypto Exchanges.
What Blockchain Technology is used for?
According to Forbes, “Blockchain is widely known to be the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, but blockchain is much more than an instrument of financial services.
The blockchain is an encrypted (with hashes) database of agreements. This means once a “deal” is made, none of the parties can go back and rewrite the terms. The use of smart contracts is a perfect example of what blockchain is used for.
Blockchain technology is now being adopted in such industries as banking,
e-commerce and retail, healthcare, charity, real estate, etc.
Let’s review some use cases.
Banking
Blockchain allows for faster transactions (less than three business days as is usually stated by banks). Moreover, transaction fees are much lower which saves money.
E-commerce and retail
Blockchain will help these industries solve fundamental problems like issues with payments, supply chain management, customer data security, and many others.
Healthcare
Blockchain technology is able to ensure transparency and integrity in such things as drug records, prescriptions, patient data storage, treatment records, records about clinical research, etc.
Charity
The Blockchain is able to prevent corruption and all kinds of malicious intents within charitable organizations. Due to transparency and immutability, people are able to track how their donations are spent.
Real Estate
Blockchain can help unify and standardize real estate records that are often incorrect and unreliable. It will be also impossible to counterfeit data for illegal purposes. All this will make the process of selling and purchasing real estate faster and more transparent. See the use case of blockchain in the land registry.
There are many more spheres that Blockchain technology can disrupt with its innovative approach to dealing with data. Think of voting, governance,
insurance, agriculture, education, entertainment, energy, climate, and environment.
Take health care and real estate as two prime examples. Health insurance automatically pays out as soon as your hospital uploads proper documentation of your illness or surgery. In the same way, a real estate deal can conclude once your bank electronically verifies the loan. Applications on a blockchain network (like Ethereum) enable this process.
One of the blockchain’s use cases is analogous to automated escrow accounts in the real world; financial services and supply chains already have seen significant blockchain adoption.
See the infographic for more;
Why you should know about Blockchain?
The days of PDFs and electronic signatures for documents are gone. Blockchain-based applications that immutably, and transparently perform routine tasks (like closing on a house) not only may render title companies obsolete, but also represent significant cost- and time-savings for accounts payable, accounts receivable, and collections departments.
These individual transactions are grouped together into blocks and are added to the database in a way that is cryptographically linked to all previous blocks. So, one big long chain of blocks, inextricably linked, that makes it impossible to change or manipulate anything that has been previously added.
The accuracy of the information on that chain is continually verified by a community of super users that are strongly incentivized to reach a consensus about the validity of that information, any anomalies (say someone trying to manipulate the data) are immediately discredited.
And importantly, the underlying information itself is encrypted, so they don’t necessarily see exactly what it is they are verifying, but can still confirm that the information is correct, and has not changed.
So what’s the point of this? Why would I want to have a public database of encrypted data? Why can’t one trusted organization just manage the database and confirm that all the information in it is in fact correct?
Well, the answer is…it can. There is nothing to stop one organization, or even a handful of organizations, from managing a database. That’s exactly how your bank knows how much money is in your current account, and an airline knows how many loyalty points you have. But there are big risks involved in doing that. You’re putting all your eggs in one basket. Conflict of
interest, corruption, data integrity, and all sorts of risks, bring us to the big revelation about blockchain. Why it really matters. Ultimately, it’s because it moves us from relying on a trustless system to a trusted one.
You no longer need to trust that your bank has been keeping proper records about the amount of money Netflix is taking off you each month, or even trust that they are looking after your money. Instead, this wealth, this value, this data, is stored digitally in an immutable ledger, free from potential corruption or human error.
So those are the fundamentals. In reality, there are a huge number of potential applications for blockchain technology. Many are complete nonsense, a few have real potential, and a tiny handful are already practicing what they preach.
How can it be used in the wider Enterprise?
Blockchain for the Internet of Things: The concept of distributing trust to a peer-to-peer network is and will continue to be essential in the world of IoT and Edge Computing. Let’s take, for instance, ZEDEDA’s vision is to create an edge economy that allows apps to run anywhere.
This means moving applications that run in data centers, where there is a single owner of all the infrastructure that provides the app developer with its entire virtual environment, to places where infrastructure is not owned by a single party but the services and data exchanges must be trusted and not spoofed.
The most prominent advantages of Blockchain are:
- Transparency and inalterability
- Data decentralization
- Security
- Speed
- Cost efficiency
- Strict operation process
Due to the hype around Blockchain, there are many people who have heard about this technology in fact, the majority of them don’t know what it is.
Some people think that Blockchain is about Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies but it is much more in reality.
The Future of Blockchain
Despite some complications and challenges, this technology has great potential for international development and worldwide adoption. Looking at the potential features blockchain possesses, in the future, we believe in discovering more values in the blockchain.