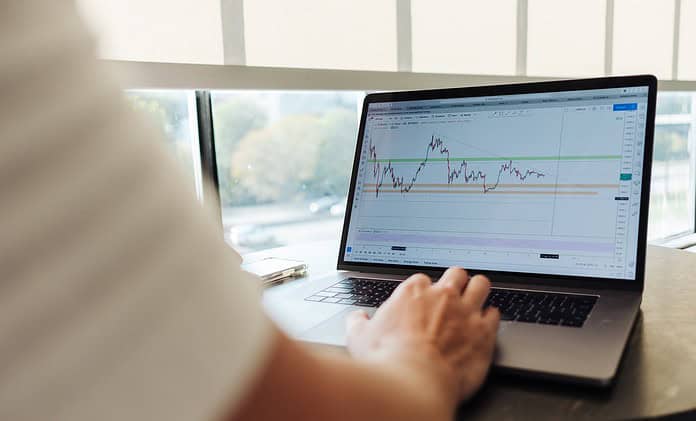
In the fast-paced world of commodities trading, achieving success in crude oil markets requires more than just luck; it demands a profound understanding of market dynamics and the implementation of advanced trading strategies.
In this article, we delve into the intricacies of crude oil trading, exploring the foundations, technical analysis, risk management, and advanced strategies that can guide traders towards prosperity. To know more about investing in oil, visit here oil-profits.com, where you will get premium investment education.
The Foundation: Understanding Crude Oil Trading
Basics of Crude Oil Market
Crude oil, often referred to as black gold, is a cornerstone of the global economy. The fundamentals of crude oil trading are grounded in the principles of supply and demand.
The intricate balance between these two factors determines the commodity’s price. Factors such as geopolitical events, OPEC decisions, and global economic health play pivotal roles in shaping the supply-demand equilibrium.
Historical Trends in Crude Oil Trading
Analyzing historical trends provides valuable insights for traders. Notable events, such as the 1970s oil crisis or the more recent volatility during the COVID-19 pandemic, showcase the impact external factors can have on crude oil prices. Learning from past trends is essential for anticipating and navigating future market fluctuations.
Mastering Technical Analysis in Crude Oil Trading
Candlestick Patterns and Trends
Candlestick patterns serve as a visual representation of market sentiment. Bullish and bearish patterns provide crucial signals for traders, aiding in decision-making processes. Recognizing these patterns allows traders to identify potential entry and exit points, contributing to a more informed and strategic approach.
Indicators and Oscillators
Technical indicators, such as the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Stochastic Oscillator, offer quantitative insights into market trends.
Traders use these tools to gauge momentum, overbought or oversold conditions, and potential trend reversals. Understanding how to interpret and apply these indicators is paramount for effective decision-making.
Risk Management Strategies for Crude Oil Traders
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Successful trading is not solely about maximizing profits but also about minimizing losses. Setting appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels is a fundamental aspect of risk management. Tailoring these levels to market conditions and understanding the psychological impact of stop-loss orders are crucial components of a comprehensive risk management strategy.
Position Sizing and Leverage
Determining the optimal position size is vital for managing risk. Calculating position sizes based on account size, risk tolerance, and market conditions ensures that traders are not overexposed to potential losses. Additionally, maintaining control over leverage is imperative to prevent excessive risk-taking, a common pitfall for inexperienced traders.
Fundamental Analysis: Navigating Economic Indicators
Key Economic Indicators Affecting Crude Oil Prices
Beyond technical analysis, understanding the impact of economic indicators on crude oil markets is essential. Indicators such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), employment data, and inflation rates influence market sentiment and, consequently, oil prices. Traders should stay informed about economic releases to anticipate potential market movements.
Analyzing Oil Inventories and Production Data
Timely access to information about oil inventories and production levels is critical for making informed trading decisions. Reports from entities like the American Petroleum Institute (API) and the Energy Information Administration (EIA) provide valuable insights into supply and demand dynamics. Traders can formulate strategies based on these reports to capitalize on market shifts.
Advanced Trading Strategies for Crude Oil Markets
Scalping and Day Trading Techniques
For those inclined towards short-term trading, scalping and day trading techniques offer opportunities for quick profits. Intraday trading strategies, such as exploiting volatility during news releases, can be effective. However, these approaches require discipline, quick decision-making, and a thorough understanding of market behavior.
Swing Trading in Crude Oil
Swing trading involves holding positions for a more extended period, typically ranging from days to weeks. Identifying swing trading opportunities requires a deep understanding of technical and fundamental analysis. Traders adopting this strategy aim to capture larger price movements while managing the inherent risks.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Staying Informed with Market News
The financial markets are dynamic, with news playing a crucial role in shaping trends. Traders must stay informed about global events, geopolitical developments, and economic releases that can impact crude oil prices. Real-time information allows for quicker reactions to market changes.
Utilizing Simulations and Backtesting
Continuous learning is the cornerstone of success in trading. Utilizing simulations and backtesting strategies enable traders to refine their skills and adapt to changing market conditions. By reviewing and improving strategies over time, traders can enhance their decision-making capabilities and increase their chances of success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the crude oil markets requires a comprehensive understanding of the fundamentals, adept technical analysis skills, and a disciplined approach to risk management. Advanced trading wisdom in crude oil markets encompasses a holistic strategy that combines historical insights, technical prowess, and adaptability to evolving market conditions.
Traders who embark on this crude wealth safari armed with knowledge and discipline are better positioned to thrive in the dynamic world of commodity trading. Embarking on the oil profit, marked by a profound understanding of market dynamics, is the key to unlocking success in the ever-evolving landscape of crude oil trading.